HydroShare: A Science Gateway for Hydrological Sciences
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What is HydroShare?
How does HydroShare work?
What is a HydroShare resource?
How do you share resources with others?
How do you create a HydroShare group?
What are HydroShare webapps?
What is JupyterHub?
Objectives
To allow the audience some experience using a scientific gateway and existing workflows
To introduce attendees to HydroShare
Exploring HydroShare

HydroShare
According to the HydroShare website, HydroShare is a web based hydrologic information system. It is developed and maintained by Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc. (CUAHSI) and was established for users to share and publish data and models. HydroShare makes this information available in a citable, shareable and discoverable manner.
This collaborative aspect of HydroShare is one of its most useful features. It enables users to work as teams in a web-based environment. Additionally, HydroShare includes tools such as web applications backed by computational resources which can be used to perform tasks on data within HydroShare. These web apps usually provide users with scientific workflows to perform computational analysis.
HydroShare has several functionalities which can provide overall research and educational advancement. These functionalities include the following:
-
Archiving and Disseminating Data
HydroShare enables users to upload and store data and corresponding metadata. Data and models uploaded into HydroShare can be assigned citation information which can be used to reference it. By permanently publishing and obtaining a citable digital object identifier (DOI) for resources in HydroShare, resources may no longer be edited and are stored in HydroShare. This data can then be discoverable and be used for reproducibility of research. This is an important feature for satisfying data management plans when research finalizes.
-
Collaboration
Users can control who the data and models are shared with. This helps users connect with other members in their research community, collaborate and receive constructive feedback about their work. HydroShare allows users to create or join groups with common research interests. By sharing data and models with other researchers in their community, users can not only connect with other colleagues within the same field, but also collaborate on research and recieve appropriate feedback from other community members.
-
Discover and Use Existing Datasets
HydroShare provides functions to help users discover data and models within its platform. It consists of a wide range of users many of which contribute data and models to users with particular research interests.
How HydroShare Works
Typical use of HydroShare includes a few steps. These include:
-
Create data
This step involves the act of collecting data. This can be collecting data using sensors, taking images, or any other method. HydroShare supports a variey of data types i.e. GIS, NetCDF, etc.
-
Upload to HydroShare
By uploading data to HydroShare, the user is provided a place to store the information and given the option to make it open and accessible. Alternatively, the user can retain privacy until ready. Uploading is simple through the web user interface. HydroShare automatically extracts as much metadata as it can from the files uploaded.
-
Describe with metadata
HydroShare enables users to annotate data with metadata. This annotation makes data interpretable and discoverable. Together, data and metadata form what HydroShare refers to as a resource.
-
Share with colleagues
Users can share data and models with individuals or make them publicly accesible. There are various method to interact with other researchers. Sharing within a group particularly, gives all members interested in a specific research topic the ability to access that resource and collaborate.
-
Permanently publish
When a HydroShare user publishes data they recieve a digital object identifyer (DOI). This enables users to cite their data resource and reference it in related journals publications. Additionally, DOI’s provide your readers with a way to find your data.
A visual of the overall process on how HydroShare is provided on their site.

HydroShare Resources
HydroShare’s website defines a “resource” as the fundamental unit of digital content in HydroShare that contains data and/or model files and their corresponding metadata. Resources act as a container into which the sharable content is placed.
Together, data, models and their metadata form the resource which acts as the single unit of digital content on which much of HydroShare’s functionality is based on. A resource can hold multiple files of different types and enables users to manage access, version, and share with colleagues and collaborative groups. Content within a resource can be either public or private, each with their own unique identifier, url, or DOI if published.
All resources within HydroShare each have their own landing page. This page displays all resource metadata and its content files. Upon logging into a HydroShare account, users can access resources they have created or that others have shared with them in the “My Resources” section.
Resource Landing Page
Users can access a resources landing page different ways.
-
They can click on resources which were discovered using HydroShare’s ‘Discover’ feature.
-
Using a direct link or citation to a HydroShare resource.
-
Additionally, users can download content files of a resource using the ‘Content’ sections download buttons.
The following figures are an example landing page for the resource titled “DEM for Hawaii” which indludes digital elevations models for Hawaii. HydroShare will attempt to fill out as much information as it can extrapolate from the files. The top of the landing page will contain information such as the author and owner of the resouce, content type, abstract and keywords associated with the resource.
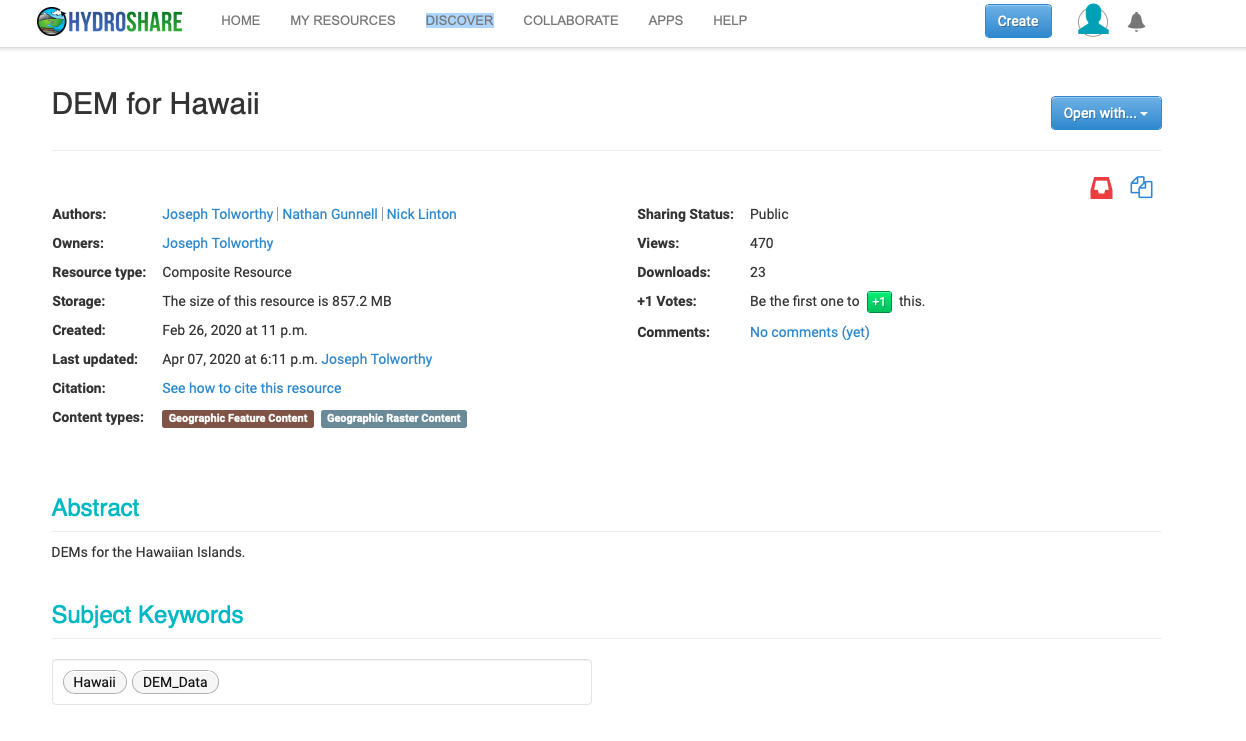
HydroShare will attempt to extract geographical information about data files if they are associated with a geographic region. Data files, models and all other accompanying data for the resource will be available in the “Content” sections.
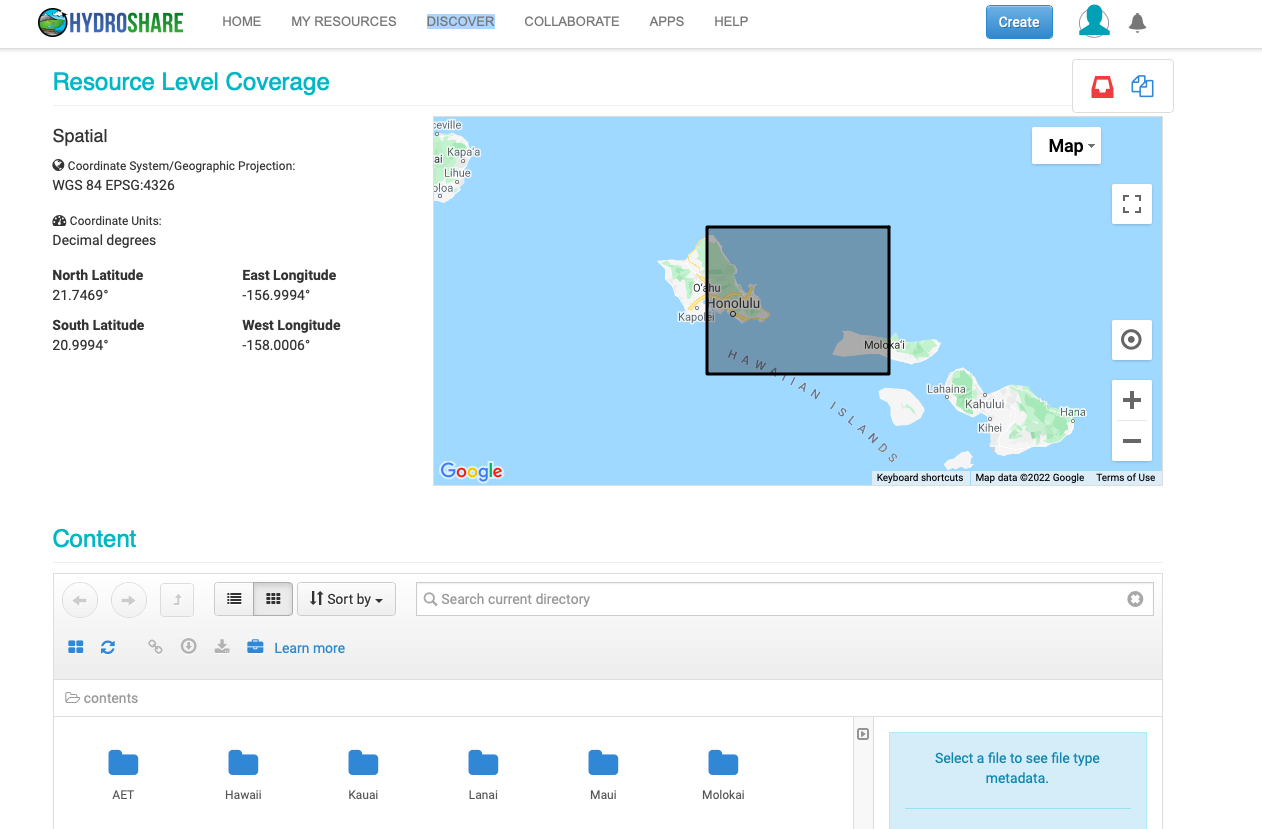
Creating a Resource and Uploading Data
In this section, readers will read about how HydroShare stores and describes data. They will also get a chance to follow along and create their own resource and share amongst other members or keep it private.
To upload data to HydroShare, users must first sign up and into their account. In the users profile page:
- Click on the Create button in the top right navigation menu.
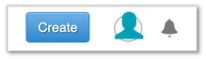
- From the dropdown, select Resource.
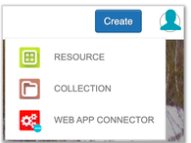
- Provide a resource title and click Create
HydroShare will create the new resource and direct to the landing page. The resource is now ready for adding files and metadata. Metadata sections within the resource include but are not limited to sections for abstract, key words, geographic coverage, references, comments, and a content section in which files are added into.
It is important to emphasize the use of metadata to the resource. It is what makes the content within it interpretable and discoverable. If making the resource public or discoverable, users must at least fill out a descriptive title, abstract, and one subject keyword.
Users should organize files into folders as needed and use descriptive names that can be used to delineate data. Also, the “Add content from the web” icon allows users to provide a link to external web resources in the case the user wants to store only metadata while data is stored elsewhere.
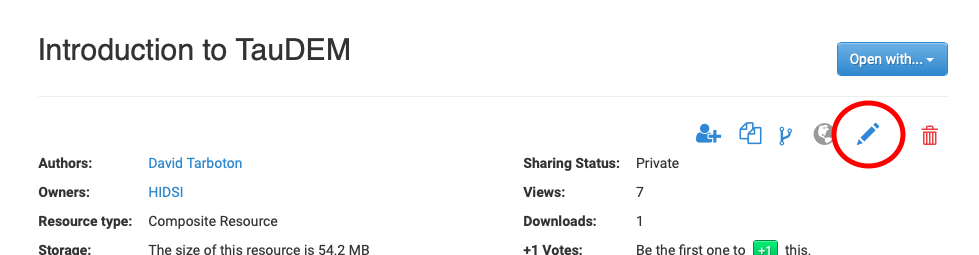
Users must have editing privileges on a resource in order to edit it. To verify if one can edit, navigate to the resource landing page and look for a pencil icon in the top right corner. If no pencil icon is visible then the user has no editing rights. Otherwise, clicking on the pencil icon will allow modification to metadata and content files. Users can also delete resources if necessary by clicking the “Delete” button on the resources landing page.
Note on published resources
Content in formally published resources can no longer be changed. Limited metadata fields can be changed. However authors, title, and content files cannot be changed.
More information on how to formally publish data on HydroShare can be found in their help documentation.
Sharing Resources
The owner of a resource can share that resource allowing HydroShare users, user groups, or the public the right to access the content and metadata of a resource. Shared resources may still be private when shared only with individual users or groups. In this case they would not be discoverable by the public.
One can access the sharing permissions by clicking the share icon in the upper right corner of the resource landing page.

Here, users can control access and sharing status. More information on sharing and privacy can be found at HydroShare’s help documentation.
HydroShare Groups and Communities
A group is a collection of Hydroshare users with a common resource landing page, that is populated by the resources owned and shared by the users in the group. A major part of HydroShare’s functionality includes ‘Groups’. You can create a Group for your research team and share resources within that group. Groups can be public or private, and you have control over what is shared with the group and what access group members have to the resources you share.
Communities are designed for groups to share resources more seamlessly, fostering public data sharing and open access. A community is a set of groups, which allows several differently administered groups to collaborate toward a common goal. Communities are ideal when a project spans administrative domains, e.g., universities, research groups, and/or businesses. Current examples of communities include collaborations between large research networks and collections of universities. As communities consist of groups, an individual user is part of a community through an associated group.
Creating a Group
To create a group:
- Go to Collaborate tab in HydroShare and click on Groups.
- Click on Create Group. – Can also search for an existing group from here.

- Fill in fields.
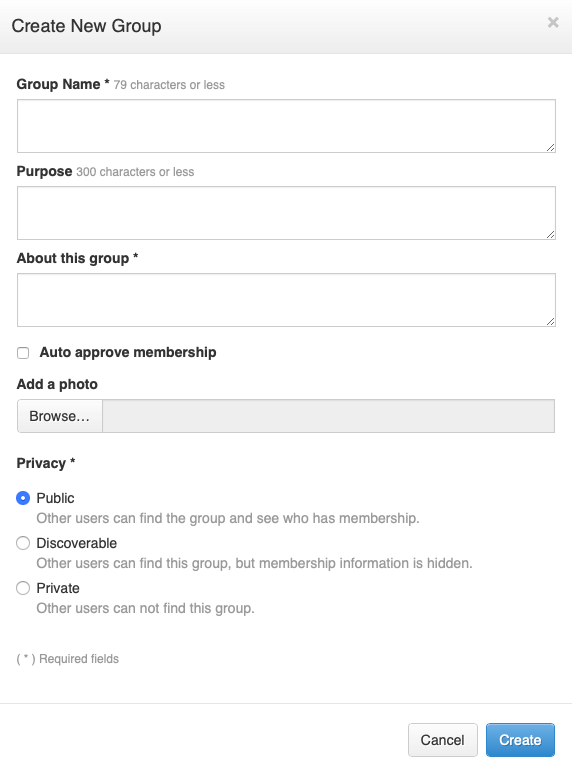
- Select access permissions.
- Click Create.
The next episode will discuss HydroShare groups in more detail.
HydroShare Web Apps
Apps are the software tools that allow you to visualize, analyze, and work with resources, more specifically data and models. Apps are hosted on separate web servers from the HydroShare website and access HydroShare resources using web services via the REST applications programmers interface (API).
Web apps are how users can work with data that is stored within HydroShare. They usually are applications which can be used to perform computational tasks or scientific workflows. Web apps run from remote servers which act as a computational backend to HydroShare. They act as tools which can be used for exploring and visualizing different types of data or performing general analysis.
Web apps communicate with HydroShare to move data in and out of it by means of a REST API. A set of apps are approved by the HydroShare development team and require account access to use. This is because they can save results that one might want to store back into their HydroShare account. Use of certain apps also requires that users join a HydroShare group associated with that web app.

CUAHSI JupyterHub
The CUAHSI JupyterHub is a web application that allows HydroShare users to execute scientific code in the cloud.
This application supports the execution of code written in several programming languages, including Python and R, and is specifically designed to support the development of research and education focused Jupyter Notebooks
Jupyter notebooks combine narrative text and code into a single document which can be used for creating and disseminating scientific workflows as well as educational tools for classroom exercises and professional workshops. The CUAHSI JupyterHub combines this functionality with the HydroShare data repository to provide a rich computational environment for water sciences.
There are multiple ways to access the CUAHSI JupyterHub web application from HydroShare. The simplest is to launch it from the HydroShare Apps library by clicking the tab labeled ‘APPS’ at the top of the HydroShare webpage.

Any data that is uploaded, downloaded, and created is associated with your HydroShare account and will persist between sessions, meaning that it will be there next time you log in.
HydroShare resources can also be “launched” into the CUAHSI JupyterHub environment. While in a HydroShare resource click the “Open with …” functionality as pictured below. This button can be found in the top right corner of any HydroShare resource landing page.
After launching the CUAHSI JupyterHub application, you will be presented with several purpose-built environments to choose from. Each of these environments contain pre-installed software to assist in the rapid development of code. You will receive the following server options:

More information on CUAHSI JupyterHub could be found in HydroShare’s help documentation.
Much of the information used here was kindly provided by the following cited sources.
Citations
- “HydroShare Support. https://help.hydroshare.org”
Key Points
Scientific gateways like HydroShare, give researchers access to domain specific data sets and workflows which can help in the analysis and visualization of data.
HydroShare provides tools to create resources which can contain data, models, workflows and other useful resources researchers can use and expand on.
HydroShare provides users simple ways to openly collaborate with the public community, privately with specific individuals, or research groups consisting of individuals with similar interests.
Webapps in HydroShare can be used to gain access to computational resources and workflows which perform data analysis tasks.