Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Overview
Teaching: 10 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What is TCP?
Objectives
Get a basic understading of TCP and why it is.
Why TCP Acts As It Does


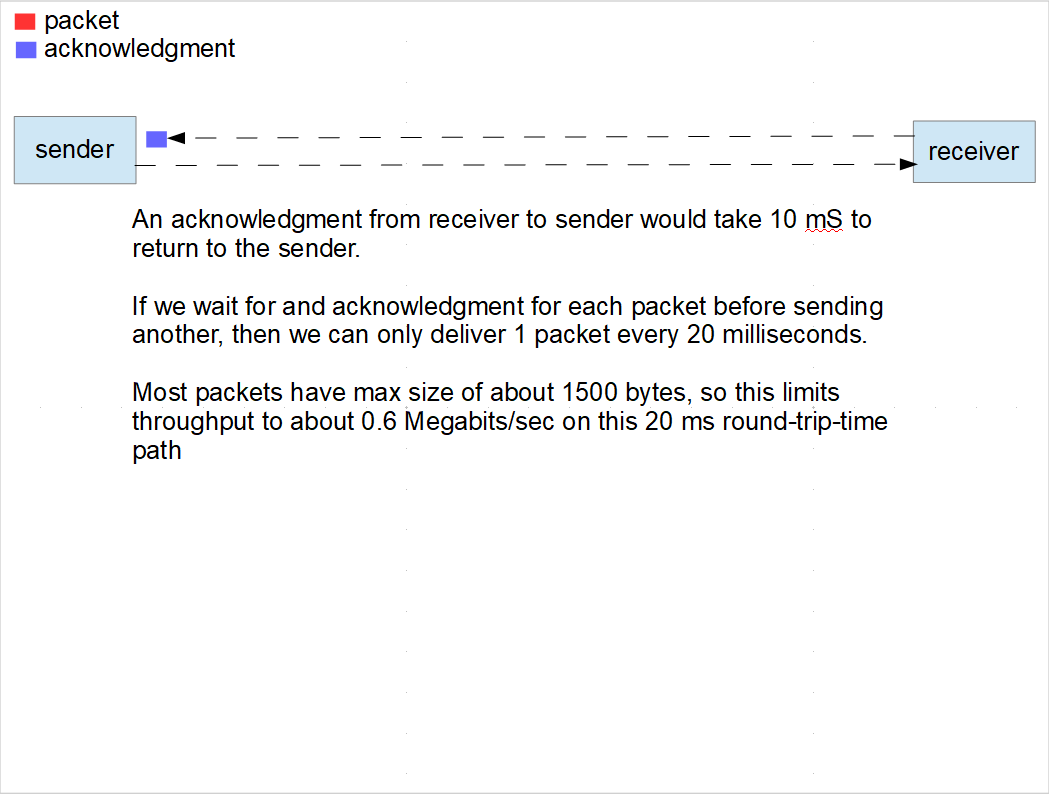



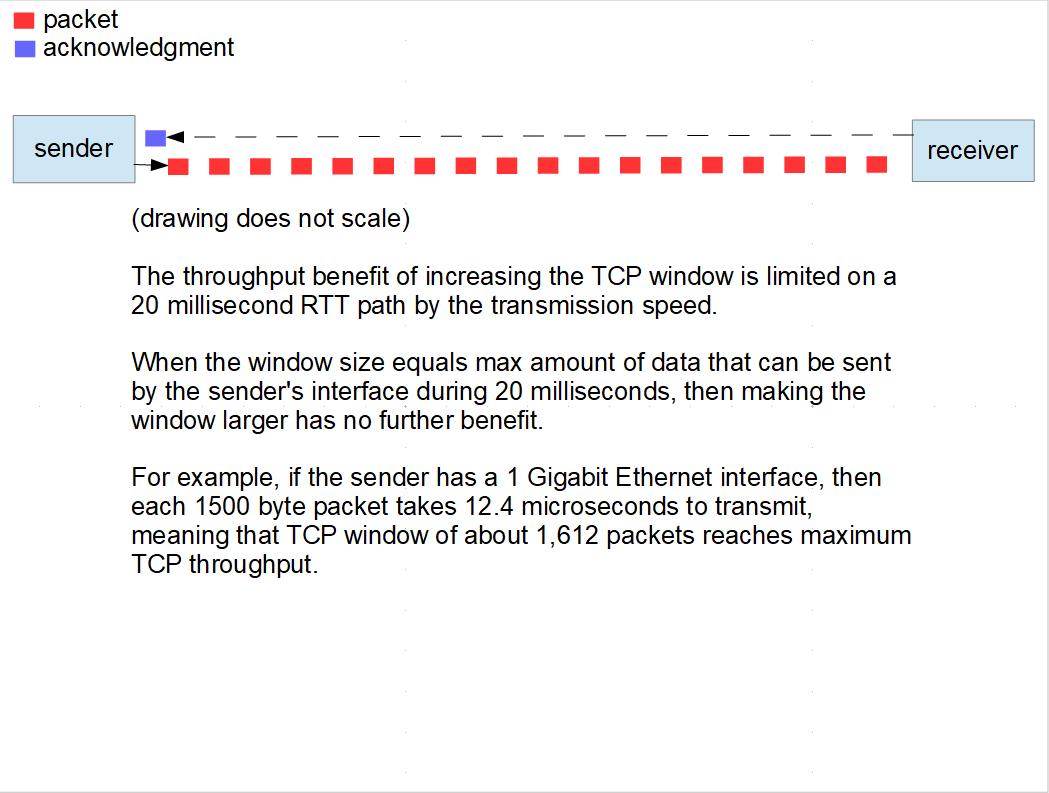







https://blog.leiy.me/post/bw-throttling-on-mac/
TCP Tuning
- Bandwidth Delay Product (BDP)
- TCP receive window = round_trip_time * effective_bit_rate
- “Effective bit rate” is usually the smallest link in a path
- Round Trip Time is propagation delay\, queuing delay\, backlog delay
- TCP RWIN max is 2 Gigabytes
- The max RTT that can support 100 Gbit/sec is 171.8 milliseconds
- Meaning: in order to go further\, you’d need more than max window
- Most modern OS auto-tune, but have limits to the auto that can be raised.
- Most default limits are insufficient for moving data fast over long distances
- Fasterdata.es.net
- A good resource for research data transfer information including TCP stuff
a couple of real-life examples to show the effect of packet pacing
4 streams, into a 12 Gbps disk system
No FQ pacing, 640 GB in 577 seconds
With no pacing, the 100 Gbps Ethernet interface sends packets in short bursts of 100 Gbps. Since our target rate is only 12 Gbps, we could distribute the packets more evenly, and possibly avoid having bursts arrive at one or more queues along the path to the receiver.
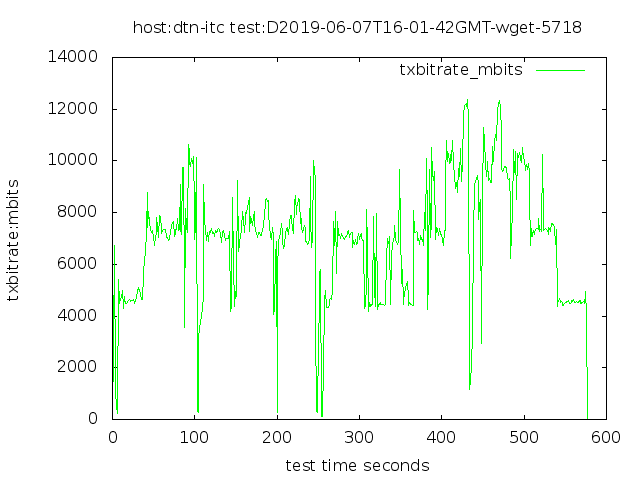

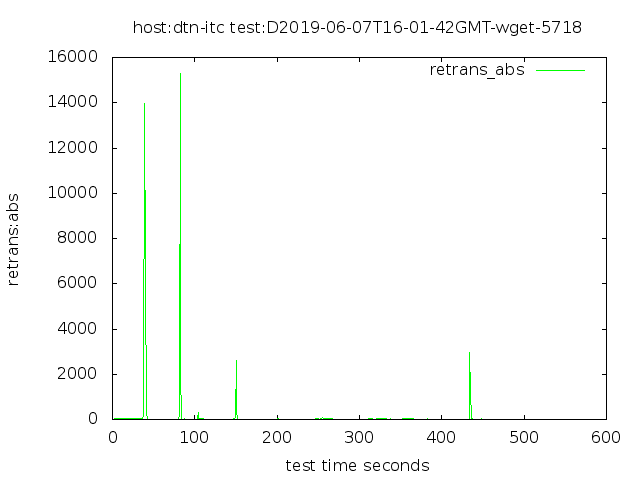

4 streams, into a 12 Gbps disk system
3Gb per stream FQ pacing, 640 GB in 487 seconds
Notice that when we pace packets at the sender to spread them out, the transfer is much smoother, and there are no more TCP retransmissions
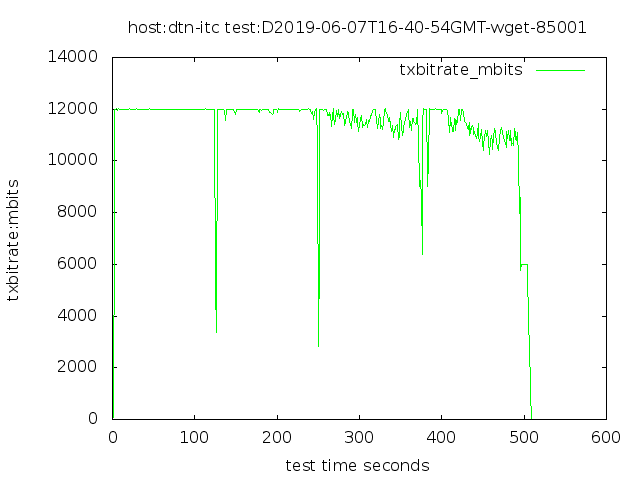

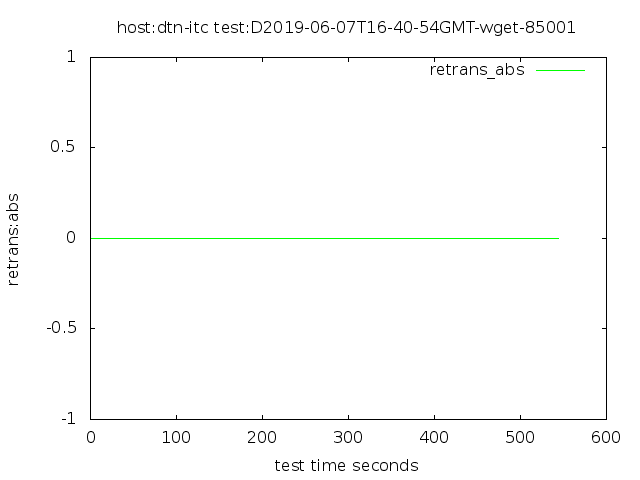

Other tuning
- Ethernet driver ring buffers
- The first and last queues in your network path
- Ethernet Offloading
- The Ethernet card does such things as TCP segmentation and checksums, relieving the computer operating system of those tasks
- Ethernet flow control – sometimes mitigates buffer issues
- Storage system (formerly “disks”) configuration
- Multi-devices under a single volume (RAID-1 or mdadm)
- high performance files systems
- If you have a fast, clean 100G network\, the next limit will be your storage throughput
- https://fasterdata.es.net/science-dmz/DTN/hardware-selection/storage/
- MTU (IP maximum transmission unit) akin to Ethernet frame size
Sometimes Less Is More
- If you experience sickly performance due to queue loss
- You might try reducing the max TCP receive window\, if you can’t affect queue pacing
- Congested paths might get more done whenpresentedwith a lower rate that doesn’t cause queue drops
- This is a temporary, stop-gap suggestion
Parallelism
Currently, up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet can be filled by a typical server grade computer
On 100 Gigabit,varioustransfer speeds > 80 Gbps have been recorded (see pic)
Working 100G flows tend to be 30 Gbps or less
Most transfers over 10 Gbps is using multiple connections
Globus GridFTP opens on the order of several hundred connections at once.

 (PUBLIC DOMAIN IMAGE: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Goodwood2007-121_The_Blue_Flame.jpg)
(PUBLIC DOMAIN IMAGE: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Goodwood2007-121_The_Blue_Flame.jpg)
Key Points
Tuning TCP can have a large impact of transfer throughput.